In today’s world, energy is at the heart of everything we do. From keeping the lights on at home to powering businesses and industries, electricity and gas are crucial to daily life. But as energy consumption continues to rise, many people are becoming more conscious of how their energy use affects their monthly bills. In this article, we’ll break down the basics of gas and electricity bills, explore trends in the renewable energy sector, and discuss how the future of energy could change the way we pay for and use these vital resources.
What Are Gas and Electricity Bills?
Gas and electricity bills are essentially invoices that detail how much you owe for the energy you’ve used in a specific time period. For most households and businesses in the U.S., these bills are issued monthly or quarterly, depending on the provider.
Gas bills typically cover the cost of natural gas used for heating, cooking, and hot water, while electricity bills charge you for the electricity consumed to power appliances, lighting, heating, and cooling systems. These bills are based on how much energy you use, and the rates can vary depending on several factors like location, provider, and the time of day you use the energy.
How Are Gas and Electricity Bills Calculated?
Understanding how your gas and electricity bills are calculated can help you make smarter decisions about energy use. There are several components that make up your bill:
- Energy Consumption: This is the amount of energy you use in kilowatt-hours (kWh) for electricity and therms for gas. Your provider will measure your energy consumption based on readings from your meter, either automatically or manually.
- Energy Rates: The cost per unit of energy (kWh for electricity and therms for gas) is determined by your utility provider. This rate can fluctuate based on demand, supply, and regulatory factors. In some cases, electricity rates are higher during peak hours and lower during off-peak hours.
- Fixed Charges: These are standard fees that cover the cost of maintaining the infrastructure needed to deliver gas and electricity to your home or business. Even if you don’t use any energy, you might still incur a minimum charge to cover these costs.
- Taxes and Fees: Depending on your state or municipality, there might be taxes and additional fees applied to your bill. These can include environmental fees, distribution fees, or even local taxes that help fund public services.
- Energy Discounts or Plans: Some providers offer discount plans, green energy options, or bundled services, which can affect your total bill. For example, signing up for a renewable energy plan might give you a discount but could also result in different charges based on the provider’s pricing structure.
Factors That Affect Your Gas and Electricity Bills
Several factors can cause fluctuations in your monthly energy bills:
- Seasons and Weather: Extreme weather conditions, like winter cold spells or summer heatwaves, can significantly increase energy consumption as heating and cooling systems work harder to maintain a comfortable temperature.
- Energy Efficiency of Your Home or Business: Well-insulated homes and energy-efficient appliances use less gas and electricity, leading to lower bills. Poor insulation, drafty windows, and older appliances can increase energy consumption and, consequently, your bills.
- Behavioral Patterns: The way you use energy in your home or business can impact your bill. For instance, leaving lights on when not needed, running the air conditioner too high, or using high-energy appliances during peak hours can raise your consumption.
- Provider Pricing Models: Energy providers may offer different pricing plans, such as fixed rates, variable rates, or time-of-use pricing. Understanding these plans can help you choose the best one for your usage patterns and potentially save money.
- Government Regulations and Energy Policies: Changes in energy policies or regulations at the federal, state, or local level can also influence the cost of gas and electricity. This includes environmental regulations, such as carbon taxes or incentives for renewable energy adoption.
The Growing Trend of Renewable Energy
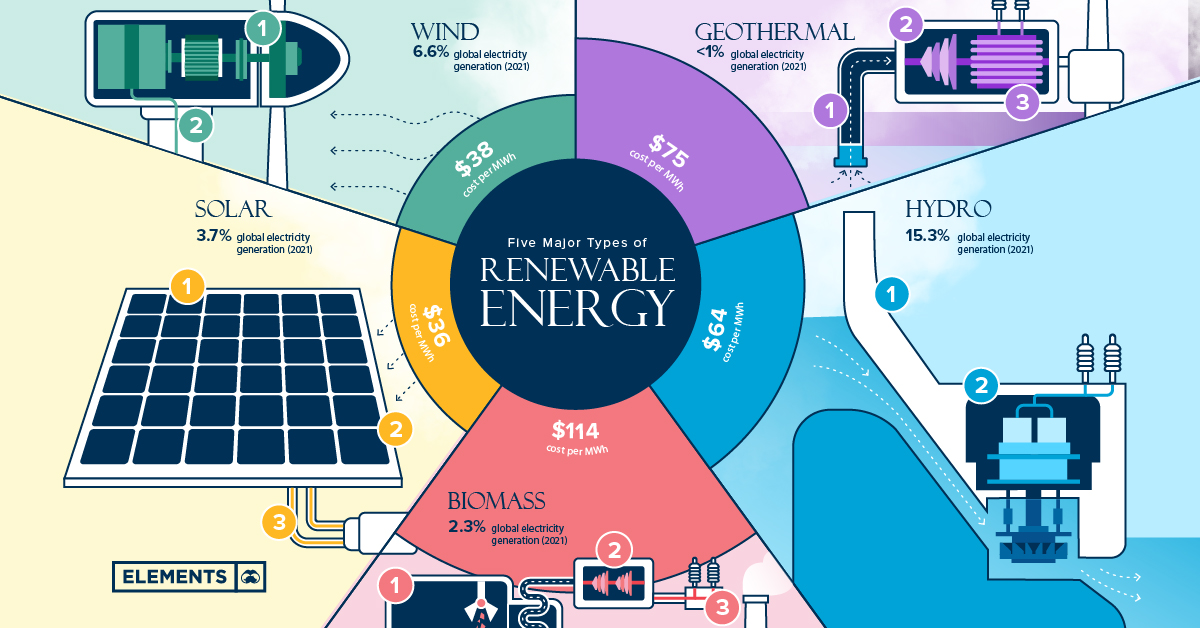
As the world shifts toward cleaner energy sources, renewable energy has become a key focus in reducing our dependence on fossil fuels like gas and coal. Renewable energy, such as wind, solar, and hydropower, is sustainable, reduces carbon emissions, and is becoming more affordable over time.
In the United States, renewable energy is playing an increasingly important role in meeting energy demand. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), renewable energy accounted for around 20% of total energy consumption in 2020, and that number is expected to grow. The rise of renewables could have a significant impact on gas and electricity bills in the future.
How Renewable Energy Affects Gas and Electricity Bills
- Cost Reductions: As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the cost of electricity generation from these sources is decreasing. Solar and wind power, for example, have become more cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. This could lead to lower electricity rates for consumers in the long run.
- Energy Independence: With more renewable energy sources integrated into the grid, the U.S. could become less reliant on imported natural gas and coal. This can help stabilize energy prices and reduce the volatility that often causes fluctuations in energy bills.
- Government Incentives: The federal and state governments are increasingly offering incentives for homeowners and businesses to adopt renewable energy technologies. These incentives may include tax credits, rebates, and low-interest loans to install solar panels, wind turbines, or energy-efficient appliances, which can lower overall energy consumption and bills.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs): With the rise of rooftop solar panels and home battery storage, consumers can generate and store their own electricity. This trend could make gas and electricity bills less of a fixed cost, allowing individuals to reduce their reliance on the grid. In some cases, consumers can even sell excess energy back to the grid, further reducing their bills.
- Smart Grids and Energy Management: The development of smart grids and energy management systems is enabling more efficient use of renewable energy. Smart grids allow utilities to better match energy supply with demand, reducing waste and lowering costs. For consumers, smart home devices can help monitor energy use and optimize consumption, leading to lower bills.
The Future of Gas and Electricity Bills
The future of gas and electricity bills will be shaped by several emerging trends in the energy sector, particularly the transition to renewable energy sources. Here are some key trends to watch:
- More Flexible Billing Structures: As renewable energy becomes more common, consumers may see new billing options, such as pay-as-you-go plans or subscription-based models. These flexible structures could make it easier to manage energy costs based on individual usage patterns.
- Increased Energy Efficiency: With advancements in energy-efficient technologies and building materials, we can expect further reductions in energy consumption and lower bills. Smart appliances, better insulation, and energy-efficient heating and cooling systems will continue to help reduce demand on the grid.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): As electric vehicles become more mainstream, households may use more electricity for charging. This could lead to changes in how electricity is priced, with time-of-use rates and special incentives for EV owners becoming more common.
- Grid Modernization: The U.S. grid is undergoing a modernization process to accommodate more renewable energy sources, improve reliability, and enhance efficiency. As the grid becomes smarter and more resilient, it could help keep energy costs stable and prevent sudden price hikes.
- Community Solar Programs: Community solar projects are gaining popularity, allowing residents to access solar power without installing panels on their property. These programs could offer a cost-effective way for people to reduce their energy bills while supporting the growth of renewable energy.
Conclusion
Gas and electricity bills are an essential part of household and business expenses, but the landscape of energy consumption is evolving rapidly. The transition to renewable energy sources is not only helping to reduce our carbon footprint but also offering opportunities for consumers to lower their energy costs. As technology continues to advance and renewable energy becomes more affordable, the future of gas and electricity bills will likely look very different from today. By staying informed about these trends and adopting energy-efficient practices, you can take control of your energy costs while contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.